This is a financial promotion for The First Sentier ASEAN All Cap Strategy. This information is for professional clients only in the UK and EEA and elsewhere where lawful. Investing involves certain risks including:
- The value of investments and any income from them may go down as well as up and are not guaranteed. Investors may get back significantly less than the original amount invested.
- Currency risk: the Fund invests in assets which are denominated in other currencies; changes in exchange rates will affect the value of the Fund and could create losses. Currency control decisions made by governments could affect the value of the Fund's investments and could cause the Fund to defer or suspend redemptions of its shares.
- Single country / specific region risk: investing in a single country or specific region may be riskier than investing in a number of different countries or regions. Investing in a larger number of countries or regions helps spread risk.
- Smaller companies risk: Investments in smaller companies may be riskier and more difficult to buy and sell than investments in larger companies.
- Emerging market risk: Emerging markets tend to be more sensitive to economic and political conditions than developed markets. Other factors include greater derivative risk, restrictions on investment or transfer of assets, failed/delayed settlement and difficulties valuing securities.
For details of the firms issuing this information and any funds referred to, please see Terms and Conditions and Important Information.
For a full description of the terms of investment and the risks please see the Prospectus and Key Investor Information Document for each Fund.
If you are in any doubt as to the suitability of our funds for your investment needs, please seek investment advice.

High-quality companies hiding in small market capitalisations
Client Update September 2023
In our last update, we touched on the idea of high-quality companies hiding in small market capitalisations in ASEAN1. This, in our view, is due to years of declining foreign-investor interest in the region. These companies are usually not covered in great detail or indeed at all by sell-side research analysts. As long-term investors, this naturally excites us as it means we can find attractive businesses that are often misunderstood or mispriced by the market.
In our experience, such companies tend to be owned and led by honest and capable people. They focus narrowly on one area where they have earned the right to compete, and they generate good returns on capital. We believe Philippine Seven is one such example.
I am a believer in anti-fragile businesses. The idea is not to catch every upturn but to survive every downturn. That is our [7-Eleven Philippines] business model. If I get a good opportunity to buy shares in Philippine Seven, I do so. I don’t invest in other stocks. I don’t have any bandwidth.
This was Jose Victor Paterno’s reply to our question regarding his purchase of around two million shares in Philippine Seven. It highlights much about what we like about him as Philippine Seven’s CEO, our alignment with management and the quality of the business. Our meeting in his office on the 7th floor of an old and inexpensive building was one of the highlights of our recent trip to Manila in March 2023 — his confidence after three brutal years of the pandemic reassured us about the recovery and trajectory of the business.
A brief history of Philippine Seven
Leading convenience store franchises in Asian markets tend to consistently earn attractive returns on capital. Examples include the 7-Elevens in Japan, Taiwan and Thailand. It has been no different for Philippine Seven. While the early years were difficult, an inflection point in the company’s history came by way of a majority investment (50.4%) from President Chain Store Corporation (PCSC) of Taiwan. The first half of the 2000s saw Philippine Seven overhaul its operations, improving its operating model, systems and processes with the help of PCSC. After this initial period, which was loss-making for the firm, Philippine Seven’s long-term track record of return on equity has been good.
By the end of 2022 Philippine Seven had more than one and a half times the number of stores of the rest of the industry combined. Its closest and most credible competitor, Alfamart, operates 1,500 outlets compared with approximately 3,500 7-Elevens. Philippine Seven has also built an extensive network of more than 20 distribution centres to cater to company-owned and franchised stores across the country. Its network is increasingly extending beyond Metro Manila and into harder-to-reach areas. All of these things, in our view, add up to a credible moat protecting future returns.
Philippine Seven
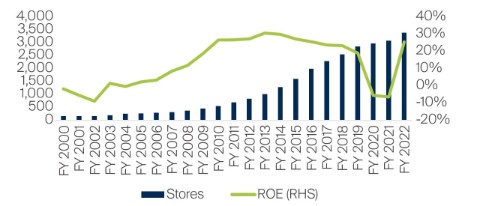
Source: Company data, Bloomberg, as at 31 July 2023. Covering Fiscal Years (FY) 2000-22. ROE is the return on equity.
Covid was an unusual and difficult period in the company’s recent history, as many stores remained closed or operated only for limited hours. Expansion and new store openings were put on hold. It offered concessions to its franchisees (PHP 711 million in 2020), which built goodwill; but the company was again loss-making in 2020 and 2021. What the management didn’t do (and rightfully so, in our view) was to shut down stores or retrench employees aggressively to preserve near-term profitability. Victor aptly described this in his letter to shareholders in Philippine Seven’s Annual Report 2020:
We have taken the view that in unprecedented times like these, stakeholders are better served by a focus on long-term market position rather than short term financial results, so long as cashflow permits. The financial results thus far, or lack thereof, reflect this view …
Looking to the future
With the pandemic (hopefully) behind us, we are seeing Philippine Seven emerge as a stronger business. The management’s quiet confidence was evident in our last meeting with them earlier this year. Revenue and profit are above pre-Covid levels and return on equity has recovered to a healthy 25%. New store additions have been picking up, with 320 added in 2022 and 380 targeted for this year. The vast majority of new stores are being added outside Metro Manila, including in the Visayas and Mindanao, where competition is limited and profitability is better. A simple comparison with the leading 7-Eleven franchises in other countries shows enough runway for years of growth.
Stores per one million population
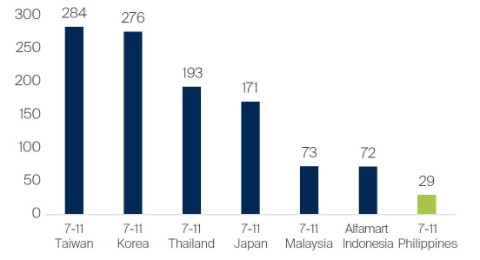
Source: Company data, as at 31 December 2022.
Of course, no company is perfect and no investment case is completely bullet-proof. Obsessing over capital preservation and about what could go wrong is at the heart of our investment process. Thus, this discussion on Philippine Seven would not be complete without mentioning our concerns.
First, while convenience stores have proven to be good businesses, retail is inherently tough. Customers’ buyingbehaviours change, formats evolve, new competitors emerge and incumbents often lose out. Alfamart is the most credible competitor today, while new formats like neighbourhood discounters DALI Philippines have also emerged. We, as well as the management, are keeping a close eye on the progress of these competitors.
The other worry lies in the execution of what the management calls a “CVS+” model (or convenience stores plus essential goods, akin to a minimart) and what that means for management bandwidth. The transition will eventually open up a large customer-purchase basket for 7-Eleven. But these changes involve a lot of work at the storefront as well as in the supply chain. It is still work in progress for the company; but, ultimately, we are backing Victor Paterno and PCSC to get it right. We are optimistic about Philippine Seven’s long-term prospects.
China + 1

Headlines in the recent media – links provided at the end of the note
In our last update, we talked about the attractiveness of Southeast Asia’s demographics as the third largest working population bloc after India and China. With the exception of Vietnam, this “demographic dividend” has been more of a dream than reality for the region over the last two decades, as manufacturing was either hollowed out (e.g., the electronics-makers in Malaysia) or never took off due to China’s rise as the “the world’s factory”.
This may soon be changing. As geopolitics force global and Chinese companies to rethink their supply chains, Southeast Asia could stand to benefit. More investments should lead to better jobs, with better incomes leading to more consumption; and eventually, more profits and value creation. That there, is something to dream about …
However, in a recent meeting, Richard Han, CEO of Hana Microelectronics, said that while everyone is excited about this shift, it will take time. There is more interest from global customers, but the issue is one of price. Electronicsrelated manufacturing in China is efficient and done at scale; and there is a 15-25% price differential for customers to digest. Meanwhile, a local ecosystem of suppliers also needs to redevelop in Southeast Asia.
The tailwinds, in our view, are real. But as bottom-up investors, we have struggled to find quality companies with sufficiently attractive risk-reward. The excitement has resulted in sky-high valuations of a handful of direct beneficiaries. Call it the scarcity premium (i.e., the lack of companies worth investing in).
For example, Delta Electronics (Thailand), a power supplies and electronic components company, is valued at 85x 2023 earnings and 24x book value. Its market capitalisation is a third bigger than its parent company, Delta Electronics, even though revenue and profits are less a third and a half respectively. Similarly Vitrox, a machine-vision inspection systems company in Malaysia, trades on 45x 2023 earnings and over 8x book value. Both companies are decent quality and are on our watch-list. But the scarcity valuation premium is well outside our comfort zone. We are staying on the side-lines for the time being.
Portfolio activity
As long-term shareholders, we do not expect to turn over the portfolio much. Good quality companies are not on sale too often. The 3-year average turnover figure for the FSSA ASEAN All-cap strategy is 16%, even including the transition in late 2021 from a predominantly Singapore-Malaysia portfolio to ASEAN. We are happy with this.
We exited a handful of smaller positions in the first half of this year. We sold out of the remaining shares in Public Bank. We think growth is unlikely to be attractive and the valuation was rich. Although we believe Public Bank is the best-quality bank in Malaysia, as evidenced by its superior asset quality and return on asset over the cycles, we had been slowly reducing our position to redeploy capital to other ideas with more attractive risk-reward. The Malaysian banking system is well penetrated with 81% household credit-to-GDP2 and 126% private sector credit-to-GDP.3 Public Bank’s loan market share in key segments is already high, ranging between 20-33%.
We exited our position in Mitra Adiperkasa after strong earnings and a share price recovery coming out of the pandemic. It has been a successful investment for us. Headline valuation is still inexpensive at 14x forward earnings, but revenue and profitability are well above prepandemic levels.

On a less successful note, we exited our investments in Thai Beverage and Venture Corporation. Although inexpensive from a valuation standpoint, we have been disappointed with the lack of progress in both companies. Thai Beverage has a complicated structure with multiple listed companies, including some that are unrelated to its core food and beverage operations. Our expectation was a journey towards a simpler structure, a better focus on existing profit engines and improved fundamental performance. This hasn’t happened and our recent meeting with the company suggested that it is unlikely as the Sirivadhanabhakdi family is happy with things as they are. We have decided to move on.
We exited Venture Corporation due to the lack of growth. While the company operates with a fortress balance sheet and solid profitability, the management doesn’t seem to be doing enough to grow. Maybe it needs a change of guard? We still have it on our watch-list and will keep an eye out for positive management changes.
We initiated a new position in Unilever Indonesia in the latter half of last year and have continued to add in the face of adversity, making it a meaningful investment. The investment in the Indonesia arm is recent, but we are very familiar with the group. Unilever plc owns 85% of the company and the group has been in Indonesia for 90 years. Ten years ago, it was a very successful and highly rated company. But, it became complacent, with very high margins and market share. As can be typical, such success led to competitors being handed a margin umbrella under which to build new businesses.
Consequently, Unilever lost market share to nimble local companies and revenues have now been stagnant for a decade. Indonesia has gone sideways as well. Fixing a problem requires acknowledgment and, encouragingly, the group have belatedly realised that they need to get back to basics. The good news is that they have appointed new top management, with multiple changes in the senior ranks, including talent from other Unilever operations (some from India). It still leads in 13 of the 15 categories it operates in, but it will need to innovate (introduce new products), reduce prices (on secondary brands) and increase share.
Turnarounds undoubtedly take time, are difficult and often not successful. We take comfort in the fact that Unilever plc has done such transformations elsewhere in its own history. Indonesia is a strategically important market for the parent and is now on senior management’s get-it-right list. We believe that the group really does care and, on that basis, risk-reward seems attractive.
We also initiated a position in Kasikornbank, the second largest bank in Thailand. Somewhat similar to Unilever Indonesia, while the investment is recent, we know the company well. Our research and meetings date back to the Asian Financial Crisis when it used to be known as Thai Farmers Bank, a reference to its post-World War II origin to provide financial services to farmers. The bank was founded by the Lamsam family who still provide stewardship as directors on the board, although ownership is now in the low single digits.
Thai banks in general and Kasikornbank in particular are seemingly loathed by investors. This is reflected in how the market is valuing it — just 0.6x the multiple of equity for a bank that is unlikely to go bust or need recapitalisation. It hasn’t been valued this cheaply since the Asian Financial Crisis.
We think Kasikornbank has a strong deposit franchise, with sticky current and savings accounts making up 82% of deposits. Its funding cost is industry-leading. It is the largest mutual fund provider and fourth largest life insurer (via 38%-owned Muang Thai Life). Pre-provision operating profit to assets (i.e., money earned by a bank before providing for bad loans and taxes on its overall asset base) is healthy at 2.5%. The challenge has been a deep and long asset-quality down-cycle for the industry. Bad loan provisions have been elevated since 2015 following populist fiscal expansion and a continued poor macroeconomic backdrop. Kasikornbank has made mistakes too, in chasing loan growth.
But, after years of poor performance, the Thai banking industry and Kasikornbank are moving towards prioritising profitability over growth. Loan growth targets are no longer sacrosanct. The aspiration is to get back to double-digit return on equity. It is early days; and we need to see the bank’s management “walk the talk”, so to speak. But we are enthused, as the market (and the valuation) doesn’t seem to expect much. If we are roughly right, provisions should decline after a decade of clean-up and returns on equity should improve from here.
Outlook and conclusion
Whilst we believe there are long-term tailwinds for the ASEAN region, we don’t profess to know which way macroeconomics and overall investor sentiment will swing in the near term. We don’t know when global interest rates will peak, for example, nor how high they might still have to go to tame inflationary pressures that have been building over the last few years. On the other hand, we would note that ASEAN central banks have been proactive in following the US Federal Reserve and country balance sheets are not showing signs of excesses, which are reasons to be sanguine.
As bottom-up stock pickers and long-term investors, we have instead focused on and draw comfort from the quality of our holdings and their largely inexpensive valuations. The companies owned in the strategy have long-term owners (or managers who act like long-term owners) as stewards of the business. We believe this often correlates with good capital allocation and operating decisions, and decent shareholder returns by extension. The average return on equity of the portfolio was 21%, as at the end of June 2023, which suggests that the ability of our investee companies to earn returns above the cost of capital, as a group, is rather reasonable.
Meanwhile, nearly 60% of non-financial companies in the portfolio do not carry any debt, after adjusting for excess cash. Another 20% have very low levels of debt (less than 25% net debt-to-equity ratio). This lack of leverage should provide the flexibility for companies to invest for the long term, as might be required, in the face of a changing external environment. While the amount of leverage in a company has not mattered much over the past decade or more, as interest rates stayed low, we think there is a distinct possibility that this will be quite different in the next three to five years.
While quality is difficult, if not impossible, to quantify in a single number or value score (and to do so would be the very definition of false precision, in our view), these metrics for the FSSA ASEAN All-cap strategy make us optimistic from both an absolute and a relative perspective on the long-term prospects for the portfolio.
We would welcome any feedback, or questions, about our investment approach or portfolio holdings. Thank you for reading.
1 Association of Southeast Asian Nations
2 Source: Bank Negara Malaysia, figure as at December 2022
3 Source: Bank for International Settlements, Total Credit to Private Non-Financial Sector, Adjusted for Breaks, for Malaysia [QMYPAM770A], retrieved from FRED, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis; https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/QMYPAM770A, August 7, 2023. Figure as at Q4 2022
Media links for the headlines in the note, in order of sequence:
https://www.digitimes.com/news/a20230704PD220/malaysia-ic-manufacturing-packaging-and-testing.html
Source: Company data retrieved from company annual reports or other such investor reports. Financial metrics and valuations are from FactSet and Bloomberg. As at 31 July 2023 or otherwise noted.
Important Information
This document has been prepared for informational purposes only and is only intended to provide a summary of the subject matter covered. It does not purport to be comprehensive or to give advice. The views expressed are the views of the writer at the time of issue and may change over time. This is not an offer document and does not constitute an offer, invitation or investment recommendation to distribute or purchase securities, shares, units or other interests or to enter into an investment agreement. No person should rely on the content and/or act on the basis of any material contained in this document.
This document is confidential and must not be copied, reproduced, circulated or transmitted, in whole or in part, and in any form or by any means without our prior written consent. The information contained within this document has been obtained from sources that we believe to be reliable and accurate at the time of issue but no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made as to the fairness, accuracy, or completeness of the information. We do not accept any liability whatsoever for any loss arising directly or indirectly from any use of this document.
References to “we” or “us” are references to First Sentier Investors a member of MUFG, a global financial group. First Sentier Investors includes a number of entities in different jurisdictions. MUFG and its subsidiaries do not guarantee the performance of any investment or entity referred to in this document or the repayment of capital. Any investments referred to are not deposits or other liabilities of MUFG or its subsidiaries, and are subject to investment risk including loss of income and capital invested.
If this document relates to an investment strategy which is available for investment via a UK UCITS but not an EU UCITS fund then that strategy will only be available to EU/EEA investors via a segregated mandate account.
In the United Kingdom, issued by First Sentier Investors (UK) Funds Limited which is authorised and regulated in the UK by the Financial Conduct Authority (registration number 143359). Registered office Finsbury Circus House, 15 Finsbury Circus, London, EC2M 7EB number 2294743. In the EEA, issued by First Sentier Investors (Ireland) Limited which is authorised and regulated in Ireland by the Central Bank of Ireland (registered number C182306) in connection with the activity of receiving and transmitting orders. Registered office: 70 Sir John Rogerson’s Quay, Dublin 2, Ireland number 629188. Outside the UK and the EEA, issued by First Sentier Investors International IM Limited which is authorised and regulated in the UK by the Financial Conduct Authority (registered number 122512). Registered office: 23 St. Andrew Square, Edinburgh, EH2 1BB number SCO79063.
Copyright © (2023) First Sentier Investors
All rights reserved.
Investment insights

- Article
- 8 mins

- Article
- 4 mins

- Article
- 10 mins